CSS Summary:
What is CSS?
CSS (Cascading Style Sheets) allows you to create great-looking web pages. Using CSS you can control exactly how HTML elements look in the browser, presenting your markup using whatever design you like.
What is CSS for?
CSS can be used for very basic document text styling — for example changing the color and size of headings and links. It can be used to create layout — for example turning a single column of text into a layout with a main content area and a sidebar for related information. It can even be used for effects such as animation.
CSS syntax:
h1 {
color: red;
font-size: 5em; }
The rule opens with a selector . This selects the HTML element that we are going to style. In this case we are styling level one headings (<h1>).
We then have a set of curly braces { }. Inside those will be one or more declarations, which take the form of property and value pairs. Each pair specifies a property of the element(s) we are selecting, then a value that we’d like to give the property.
Before the colon, we have the property, and after the colon, the value. CSS properties have different allowable values, depending on which property is being specified. In our example, we have the color property, which can take various color values. We also have the font-size property. This property can take various size units as a value.
How To Add CSS?
There are three ways of inserting a style sheet:
- External CSS
- Internal CSS
- Inline CSS
External CSS:
With an external style sheet, you can change the look of an entire website by changing just one file!
Each HTML page must include a reference to the external style sheet file inside the element, inside the head section.

An external style sheet can be written in any text editor, and must be saved with a .css extension. and should not contain any HTML tags.
Internal CSS:
An internal style sheet may be used if one single HTML page has a unique style.
The internal style is defined inside the

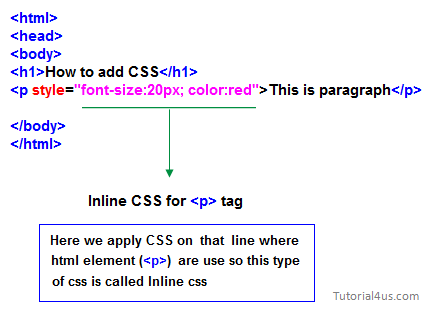
Inline CSS:
An inline style may be used to apply a unique style for a single element.
To use inline styles, add the style attribute to the relevant element. The style attribute can contain any CSS property.
Summary of the 3 types:

Multiple Style Sheet:
If some properties have been defined for the same selector (element) in different style sheets, the value from the last read style sheet will be used.
Cascading Order:
All the styles in a page will “cascade” into a new “virtual” style sheet by the following rules, where number one has the highest priority:
- Inline style (inside an HTML element)
- External and internal style sheets (in the head section)
- Browser default
So, an inline style has the highest priority, and will override external and internal styles and browser defaults.
CSS color Property:
body {
color: red;
}
h1 {
color: #00ff00;
}
p.ex {
color: rgb(0,0,255);
}
CSS Syntax:
| color: color | initial | inherit; |
| value | Description |
|---|---|
| color | Specifies the text color |
| initial | Sets to its default value |
| inherit | Inherits from its parent element |